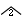- HOME
- Publications
- Materials Transactions
- Manuscript Instructions
Manuscript Instructions
| 1. Styling of manuscript |
| MS-Word templates download |
| EndNote style download |
| 1.1. Typing style |
| 10.5 pt standard, line pitch 22 pt, 22 lines per page are preferred. |
| 1.2. Manuscript arrangement |
| (1) | On the first page, the Graphical Abstract should be displayed. |
| (2) | On the second page (cover page), the following should be typed: 1) Title, 2) Authors, 3) Affiliation, 4) English synopsis, 5) blank two lines and 6) Keywords. |
| (3) | From the next page onwards, the contents should be in the following order: 1) Main text, 2) Acknowledgement, 3) List of References, 4) Appendix and 5) List of captions of Tables and Figures. Each part should be typed on separate sheets. Then 6) Tables and Figures should follow, on separate sheets. | ||||||||
| 1.3. Page numbering | |
| · | Page numbering should be made at the bottom center of each sheet from the cover page onwards, in the order: Main text, Acknowledgement, Appendix, List of References, List of captions Tables and Figures, Tables and Figures. |
| 2. Manuscript-making | |
| 2.1. Title | |
| (1) | The title of the paper should be determined such that it reflects the contents most suitably and concisely. |
| (2) | Abbreviated symbols, if not conventionally used, should be avoided. |
| (3) | Description of element symbols |
| · | When an element name is used as a symbol of material, the use of element symbols should be avoided and the name of the element should be fully spelled out. |
| · | When the element name is used as chemical symbol or adjectively used, the element symbol can be used. |
| (4) | Expressions such as “Study on” or “On the” should be avoided as the start of the title. |
| (5) | Definite articles and indefinite articles are used as less as possible. |
| (6) | The first letter of a word other than prepositions, conjunctions and articles are all capital letters including hyphen-connected words. |
| 2.2. Description of authors |
| Both the first name and last name should be written out fully. Middle names can be abbreviated. |
| 2.3. Description of affiliations |
| (1) | When authors belong to different research organizations, each organization should be designated by superscript numbers, in the form 1, 2 etc. The name of the department, name of the organization, and the address should be fully written out and should be separated by commas. The postal zip code and country name should also be given. |
| (2) | The name of the research organization should be given under the names of the authors. |
| (3) | When an author's present affiliation is different from the name of the organization, in which the research was performed, it should be expressed as a footnote using an asterisk. |
| (4) | For graduate students and undergraduate students, the affiliation should be expressed as a footnote using an asterisk. |
|
| (Footnote) | *1 | Graduate Student, A University |
| *2 | Graduate Student, A University. Present address: Corporate Research and Development Laboratories, B Co. Ltd., Sendai 980-0001, Japan |
| 2.4. English synopsis |
| Numeral equations and references cannot be designated by numbers. |
| 2.5. Keywords |
| Except for proper nouns, all letters should be small letters. |
| (1) | It is advisable to select keywords from the title and synopsis, since these contain important words. However, keywords can also be selected from other parts of the manuscript. |
| (2) | Keywords should be selected so as to be concrete meaningful words with as narrow definition as possible. Critical, Stress →critical stress Life→tool life, fatigue life |
| (3) | Use of keywords in noun form Studied experimentally→ experimental study |
| (4) | Name of elements, name of chemicals, name of compounds and so forth should be fully spelled out instead of using the symbol of the element. CrMo steel→chromium molybdenum steel E→Young's modulus, modulus of longitudinal elasticity |
| (5) | Simplified symbols and abbreviated forms cannot be used. ESR |
| (6) | Use of compounded words and phrases is restricted to those that are commonly used. |
| (7) | Be careful not to omit popular words. |
| (8) | In the case that the authors have difficulties of whether to select or not, please select them as keywords. |
| 2.6. Heading of body |
| large size heading: | 1. 2. ··· |
| middle size heading: | 1.1 2.1··· |
| small size heading: | 1.1.1 2.1.1··· |
| (1) (2)··· | |
| (a) (b)··· |
| 2.7. Tables and figures |
| Tables and Figures (photographs) are to be provided in one of the following file formats, and are to be submitted together with the manuscript. When the designated files are not available, completed figures are accepted for image processing. (No freehand drawings will be accepted.) |
|
Adobe Illustrator (save as version 10) PSD (All layers are combined) EPS (PostScript level 1 compatibility) PICT (Macintosh) JPEG (high resolution, low compressed) TIFF PNG GIF (not see-through, assign all colors) Microsoft Word/ Excel/ PowerPoint PDF (no down sampling and no compression, All fonts must be embedded) |
| 2.7.1. Tables |
| (1) | Each Table should be made on a separate sheet. Tables are set after the list of captions of Tables and Figures in submission. Tables should be numbered sequentially. |
| (2) | Tables should be sequentially numbered in the following manner: Table 1, Table 2. |
| (3) | The Table caption should be located at the top of the Table, starting with a capital letter and ending with a period. |
| (4) | Headings in the Table should begin with a capital letter. |
| (5) |
Size of Table: Same as the publication size. Half width size figure: 7-8 cm in width, 12 point letter size, subscript 10 point size Full width size figure: 10-13 cm in width, 12 point letter size, subscript 10 point. The lines are of the same dense and their width is of 0.5 pt and up (0.18 mm and up). The vertical line is not displayed as a general rule. |
| (6) | Space between letters should be arranged not by auto-spacing but by space key, to avoid broken layout. |
|
|
|
| Thermal conductivity, κ/Wm-1K-1 | |
|
|
|
| TiB2 | 69.9(1300 K) |
| TiC | 30.0(1773 K) |
| TiN | 67.8(1773 K) |
| ZrB2 | 64.5(1300 K) |
|
|
|
| 2.7.2. Figures including photographs | |||||||||
| (1) General instructions | |
| 1) | Each Figure should be drawn on each separate sheet. |
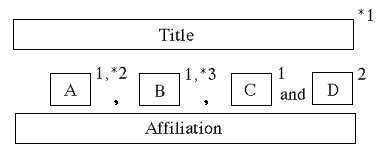
| 2) | Figures should be sequentially numbered in the following manner: Figure 1, Figure 2. If a figure is divided to several parts, each part should be labeled as follows: (a), (b), (c). |
The locations of (a), (b), (c) are either of follows.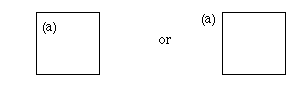
|
|
| 3) | Figure caption is made under the figure, starting with a capital letter and ending with a period. |
| 4) | The original photograph should not be of a once-half-tone type. Clear contrast, and vivid lines and contours are required. |
| 5) | Additional charge is not needed to publish figures/tables in color. |
| 6) | If a color figure is printed in black/white, soft colors could become hard to see. Please check wash-out or blurriness before submission. |
| (2) Drawing instruction | |
| 1) | Specifies the necessary scale for the photographs. |
| 2) |
Size of figure: Same as the publication size. Half width size figure: 7-8 cm in width, 10 point letter size, subscript 8 point size Full width size figure: 10-13 cm in width, 10 point letter size |
| 3) | Letters in the figure should be the same size. |
| 4) | Meshing consisting of thin, gray lines or very fine lines, and dense curve lines which may cause moire fringe phenomena, are not recommended. |
| 5) |
The lines are of the same dense and their width is of 0.5 pt and up (0.18 mm and up). The framework lines are made not by broken lines but solid lines. |
| 6) | Space between letters should be arranged not by auto-spacing but by space key, to avoid broken layout. |
| (3) Graphical Abstract | |
| 1) | In addition to the text abstract, Graphical Abstract (hereafter GA) which represents the contents of your paper best should be displayed. GA will be only on the J-STAGE Online Journal. |
| 2) | Authors can select an original figure or a photograph as well as the one used in the paper. GA can contain captions or additional words. Specific file format is as follows: File type: jpg, gif, or png File size: up to 100MB Resolution: 700 pixel x 700 pixel (more than 300 dpi) Color: as submitted Sample |
| 3) | The figure or photograph which will be used as GA should be clearly stated paper’s on submission, indicating as “Graphical Abstract” at the header of the manuscript sheet. Caption should start with “Caption:”. During review process, the Editorial Committee judges whether a selected GA is appropriate for each paper. |
| 4) | The color tone of GA is the same as submitted or as the one displayed in the text body. |
| 5) | Words or sentences in the figure will be shown as submitted. |
| 6) | Authors proofread GA as well as the text or figures. |
| 7) | GA does not need any additional costs including Color Charge. |
| 2.8. Footnotes and References | |
| (1) | No footnotes are allowed in the main text. Comments and notes are to be shown in the references. |
| (2) | Oral presentation should not be shown in the footnotes. If it is needed, quote the abstracts or proceedings in REFERENCES. |
| (3) | Citation of references should be made sequentially, in the form [1, 2] or [3-6]. List of References should be attached. |
| (4) | One reference number should correspond to one reference. Even if another reference of the same author is cited, allocate a different reference number and do not use the expression, “ibid”. |
| (5) | A reference is described in the order: names of authors (no need of comma before “and”), title, the abbreviated name of the journal, volume number (year), page. Volume number should be expressed in Gothic type, and the names of books in italics. The abbreviation of journals should follow the ISO standard. The Abbreviation of Journals |
| (6) | When authors are 15 or less, all of the names should be given, instead of using “et al”. |
| Example of journal | |
| [1]S. R. Pati and M. Cohen:Nucleation of the isothermal martensitic transformation Germination de la transformation martensitique isotherme Die keimbilditng der isothermen martensitischen umwandlung, Acta Metall. 17 (1969) 189-199. | |
| [2]W. Köster, T. Gödecke and D. Heine:Der Aufbau des Systems Kupfer-Indium-Zinn ım Bereich von 100 bis 50 At.-% Cu, Z. Metallk. 63 (1972) 802-807. | |
| Example of book | |
| [3]W. Hume-Rothery, R. E. Smallman and C. W. Haworth: The Structure of Metals and Alloys, (The Metals and Metallurgy Trust of the Institute of Metals and Institution of Metallurgists, London, 1969) pp. 336-342. | |
| [4]E. Houdremont: Handbuch der Sonderstahlkunde, 3. Aufl., 2. Bd., (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1956) pp. 934-939. | |
| Example of Proceedings | |
| [5]C. Wagner:Thermodynamics of alloys,Steelmaking, The Chipman Conference, ed. by J. F. Elliott, (The M.I.T. Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts, 1965) pp. 19-25. | |
| [6]J. Ishihara and I. Ikuta: The non-uniformity of amorphous ribbon made by double roller quenching method, Proc. 4th Int. Conf. on Rapidly Quenched Metals,(The Japan Inst. Metals, Sendai, 1982)pp. 19-25. | |
| [7]D. Schryvers: Quantifying 3D precipitate distributions and strain fields in Ni-Ti SMA with different processing conditions, Collected Abstracts of the 2010 Spring Meeting of the Japan Inst. Metals(2010)p. 213. | |
| [8] T. Kinzoku: Microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg alloys, Collected Abstracts of the 201x Spring ( Autumn) Meeting of the Japan Inst. Metals 2011 No. xx (DVD) | |
| Example of Government report | |
| [9]A. Colloza and J.L. Dolce: NASA/TM2005-213427, (NASA Glenn Research Center 2005), p.22 (online) | |
| Example of Webpage | |
| [10]"Grants.gov Application Guide SF424 (R&R)". U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. http://grants.nih.gov/grants/funding/424/SF424_RR_Guide_General_Adobe_VerC.pdf, (accessed 201x-04-28) | |
| Example of Online database | |
| [11]MMDB-Entrez's Structure Database. National Library of Medicine, National Center of Biotechnology Information. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/MMDB/mmdb.shtml, (cited 201x-04-28). | |
| Example of footnotes | |
| [12]1 eV=1.60218×10-19J | |
| 2.9. Numerical equation | |
Numerical equations in the main text should be expressed as, for example, x/3, a/(b + c) instead of 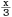 , , 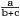 . . | |
| The exponential symbol should be expressed as “exp”, if possible. | |
| The expression of 4×10-2 is used instead of 4 ·10-2. |
| 2.10. Decimal point and thousand-unit comma | |
| The decimal point for numerals should be put at the lower level of a numeral. The thousand-unit comma should not be used to prevent confusion with decimal points. |
| 2.11. SI Unit |
| (1) | Usage of SI units should be, on the whole, based on Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS). SI Units Conversion Table |
| (2) | Among units which are not included in SI units but are permitted for combined usage in JIS, only the following units can be used. |
| (a) | Units which can be used for combined usage because of their practical importance.
| ||||||||
| (b) | electron volt which can be used with SI units, in certain academic fields. (However, it should be used only after the expression by J and be shown inside parentheses.) | ||||||||
| (c) | following units can be used mass fraction in percentage mass% volume fraction, as a percentage vol% volume fraction, as a parts per million vol ppm | ||||||||
| NOTE : Celsius is a proper unit for temperature and is a SI unit | |||||||||
| 2.12. Numerical, Roman and Greek letters used for Tables and numerical equations |
| (1) | Numerical, Roman and Greek letters used in Tables and numerical equations should be typed clearly to prevent misunderstanding. Superscript, subscript, Greek letters, italics, bold letters and so on, should be designated only in the original manuscript used for printing by red ink.(In copies of the manuscript, these letters are not needed, to prevent inconvenience in the reviewing process.
| |
| (2) | Letters representing numeral values (quantity symbols) should be designated regardless of whether they are constants or variables, since they are printed in italic letters. Mathematical symbols are designated by Roman letters.
Examples: quantity symbols: length; l, area; A, S, volume; V, v, pressure; P, force; F, time; t, vector; A, a, scientific constants; N, k mathematical symbols exponential function; exp (when expressed by e, it is printed in italic letters) natural logarithms; ln x general logarithms; log x sine; sin cosine; cos tangent; tan |
| 2.13. Acknowledgments |
| Acknowledgments should be made at the end of the manuscript, leaving an interval of one line after the body of the text. Financial assistance, the use of apparatus and the receipt of research funding and so on, should all be acknowledged in this section. |
| 2.14. Appendix |
| Tables and Figures and equation numbers in the Appendix, should be numbered separately from the numbering in the main text, by writing: A1, A2, etc. |
| 2.15. Supplementary materials |
| Authors can upload original data of figures/tables, information that cannot be included main text etc. as supplementary materials of a manuscript in online journal. To publish supplementary materials, authors should submit a file of supplementary materials together with the manuscript. The format of supplementary materials is as follows: - Size of file: 5MB or less - Number of file: one per paper - Type of file: PDF *Add a headline as “Supplementary materials” on the first page. *The language should be English. The editorial committee will check the contents of supplementary materials as well as the contents of the paper itself. Supplementary materials will be published as it is, without proofreading: authors should have responsibility on the contents and format of supplementary materials. |
| 2.16. Approximation of printed page number |
| Title, authors, affiliation: about 40 lines in the body English synopsis: one line in printed form of 16-20 words corresponds to about 40 words in the main text. The main text: one page in printed form corresponds to about 1000 words or 6000 letters. |




 , Cr
, Cr